Automated process control is transforming industries worldwide. According to the International Society of Automation (ISA), 70% of manufacturers are leveraging automation to enhance productivity. This technology minimizes human intervention, leading to more consistent quality and efficiency. Reports show that companies using automated systems can increase production rates by up to 30%.
However, the implementation of automated process control is not without challenges. Many organizations face integration issues with existing systems. Furthermore, training staff to adapt to new technologies remains a significant hurdle. Some companies report a 20% increase in operational costs during the transition phase. Reflecting on these obstacles is crucial for meaningful improvement.
Moreover, industries must consider long-term impacts on their workforce. While automation streamlines operations, it can lead to job displacement. Balancing automation with human skills is essential. Companies should strategically approach automated process control to ensure sustainable practices. This careful planning is vital as the landscape of industry continues to evolve.

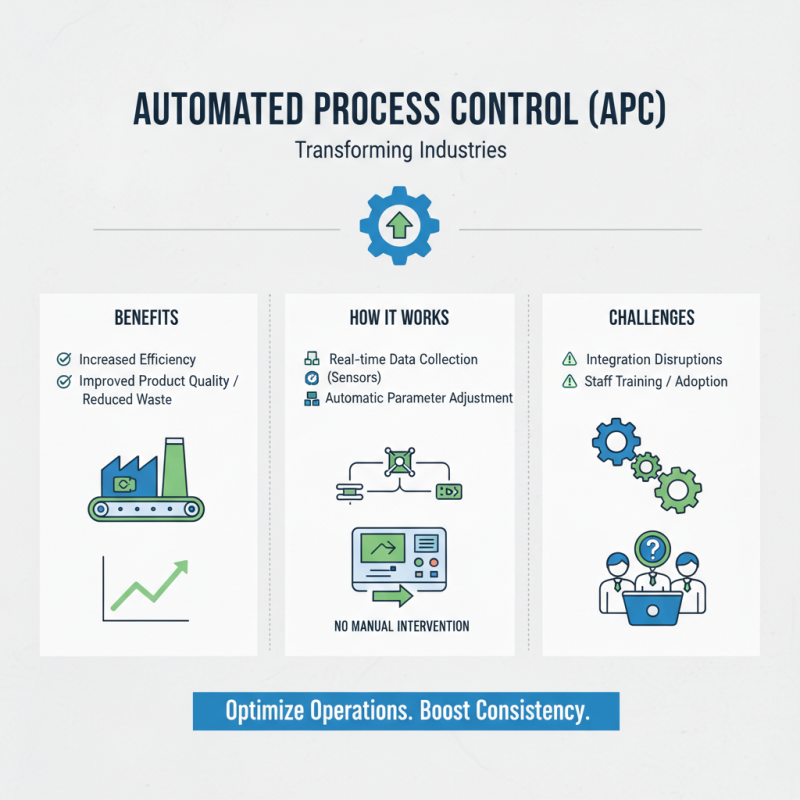
Automated process control (APC) has transformed various industries, enhancing efficiency and consistency. In manufacturing, for instance, APC optimizes operations by reducing waste and improving product quality. Sensors collect data in real-time, adjusting parameters as needed. This system allows for adjustments without manual intervention. However, some companies struggle with implementation. Integrating new technology can disrupt existing workflows. Staff training is crucial to ensure everyone understands the system.
In the chemical industry, APC ensures safety and accuracy. By monitoring pressure, temperature, and flow rates, processes remain in control. This minimizes human error. But achieving precision can be challenging. Sometimes, equipment malfunctions or data inconsistencies arise. Industries must be ready to troubleshoot these issues regularly. Continuous monitoring and analysis are vital.
Food processing also benefits from APC. It maintains product quality and hygiene standards. Automated systems regulate cooking times and temperatures. Yet, industries face obstacles. High initial costs can deter smaller businesses. They may lack the resources to invest in automation. Companies must weigh the benefits against the challenges. Finding the right balance is essential for success.
Automated process control systems are becoming essential in various industries. To implement these systems effectively, several key technologies need to be considered. One of the most significant is sensors. Sensors provide real-time data on critical parameters. They can help monitor temperature, pressure, and flow rates. Accurate data is crucial for making informed decisions.
Another important technology is control algorithms. These algorithms process the data collected by sensors. They make adjustments to maintain optimal operation conditions. However, the implementation of these algorithms can be complex. It requires careful testing and adaptation to the specific processes used in your industry.
Tips: Focus on integrating user-friendly interfaces. Simplifying data visualization can enhance decision-making. Ensure training for staff members is comprehensive, as their input is vital. Regularly revisit the automation process to identify challenges. Automation should evolve continuously to adapt to new requirements.
In addition, data analytics plays a critical role. Analyzing historical data helps identify patterns and predict future behavior with greater accuracy. Yet, many businesses may overlook the importance of data quality. Poor-quality data can lead to inefficient control actions, resulting in production losses and increased costs.
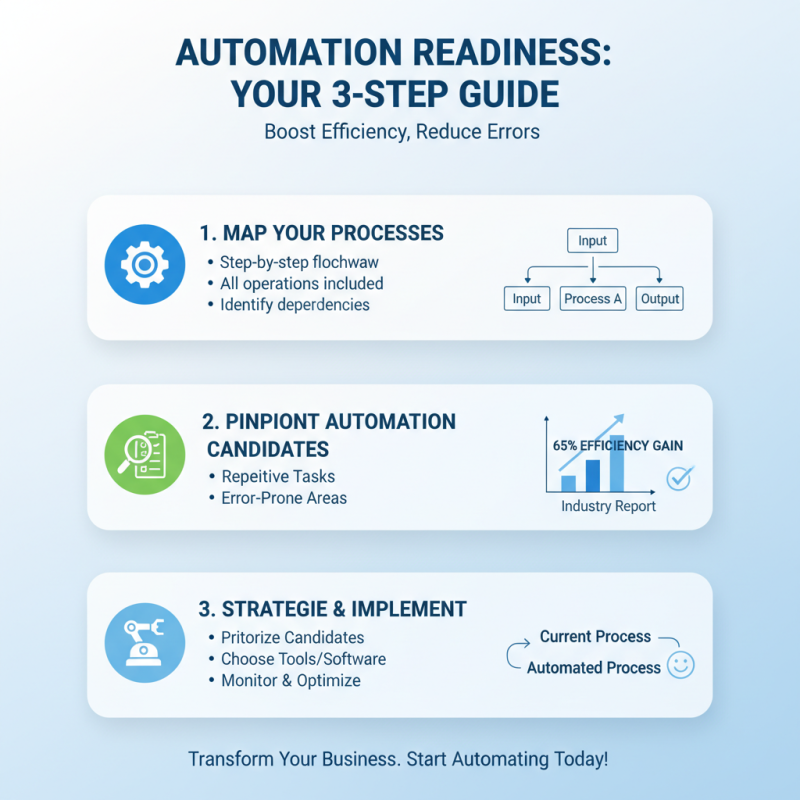
Assessing your current processes is vital for automation. A recent industry report reveals that 65% of companies see improved efficiency after automation. Begin by mapping out each step in your current operations. Identify areas that involve repetitive tasks or are prone to errors. These are prime candidates for automation.
Tips: Focus on data collection. Use metrics to evaluate performance. Consider how long each task takes. This data will guide your decisions. Engage with team members. They can offer insights on pain points that automation could alleviate.
Don't overlook the importance of flexibility. Processes may require adjustments after automation. Regularly review and refine your systems. In some cases, automation can lead to complexities, requiring ongoing monitoring. Strive for simplicity; too many automated steps can create confusion. Remember, automation is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each industry has unique challenges that need tailored approaches.
Automated process control (APC) has gained traction in various industries. One significant factor driving its adoption is cost-effectiveness. Data from a recent industry report indicates that APC can reduce operational costs by up to 30%. This substantial decrease stems from improved efficiency and reduced waste. Moreover, companies can expect a return on investment (ROI) of about 5-7 times their initial expenditure within a few years.
Nonetheless, the transition to APC is not without challenges. Many plants face high initial investment costs. A study highlighted that 25% of companies reported delays due to budgeting issues. Furthermore, employee training can pose additional expenses. A survey showed that nearly 40% of industries underestimated the amount of training needed, leading to operational disruptions. These factors warrant careful consideration before implementing APC systems.
Integration into existing processes remains complex. Organizations must assess their specific needs and existing infrastructure. The success of APC relies on a tailored approach. Some reports suggest that up to 35% of industries encounter integration issues, revealing gaps in technology compatibility. Thus, while the benefits are clear, companies must approach adoption thoughtfully.
| Criteria | Before Automation | After Automation | Cost Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Costs | $150,000 | $100,000 | 33% |
| Material Wastage | $50,000 | $30,000 | 40% |
| Downtime Costs | $75,000 | $20,000 | 73% |
| Quality Issues | $40,000 | $10,000 | 75% |
| Total Cost Savings | $315,000 | $160,000 | 49.84% |
In the manufacturing sector, automation has transformed how companies operate. A car manufacturer implemented automated systems on the assembly line. This led to increased efficiency and reduced production time. However, the change did not come without challenges. Some employees struggled to adapt to new technologies. Initial resistance from the workforce highlighted the importance of training.
In another example, a food processing company integrated automation to improve quality control. Sensors were set up to monitor product consistency. This minimized human error and enhanced safety. Yet, issues arose when the system malfunctioned. Production was halted for hours, illustrating the need for robust backup plans. Regular maintenance and updates are crucial in automation processes.
Even with successful cases, the journey remains complex. Full automation can create gaps in the workforce. Finding a balance between labor and technology is vital. Moreover, the long-term cost-effectiveness of these systems must be continuously evaluated. Automation brings immense benefits, but it also requires careful consideration and adaptation.
This chart illustrates the automation adoption rates across various industries. Manufacturing leads with a 70% adoption rate, followed by healthcare at 65%. Finance, retail, and telecommunications show varying levels of adoption, highlighting the diverse approaches to automation across sectors.